Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite UNION operator to combine result sets of two queries into a single result set.
Introduction to SQLite UNION operator
Sometimes, you need to combine the results of multiple queries into a single result set. To achieve this, you can use the UNION operator.
Here’s the syntax of the UNION operator:
query1
UNION [ALL]
query2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, specify the first query.
- Second, use the UNION operator to indicate that you want to combine the result set of the first query with the next one.
- Third, specify the second query.
The UNION operator eliminates duplicate rows in the final result set. If you want to retain the duplicate rows, you can use the UNION ALL operator.
Here are the rules for the queries when using the UNION operator:
- The queries (
query1andquery2) have the same number of columns. - The corresponding columns must have compatible data types.
- The column names of the first query determine the column names of the combined result set.
- If you use the
GROUP BYandHAVINGclauses, they will be applied to each query, not the final result set. - If you use the
ORDER BYclause, it will be applied to the combined result set, not the individual result set.
Note that the difference between UNION and JOIN e.g., INNER JOIN or LEFT JOIN is that the JOIN clause combines columns from multiple related tables, whereas the UNION operator combines rows from multiple result sets.
Suppose you have two tables t1 and t2 with the following structures:
CREATE TABLE t1 (c1 INT);
INSERT INTO
t1 (c1)
VALUES
(1),
(2),
(3);
CREATE TABLE t2 (c2 INT);
INSERT INTO
t2 (c2)
VALUES
(2),
(3),
(4);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement combines the result sets of the t1 and t2 tables using the UNION operator:
SELECT c1 FROM t1
UNION
SELECT c2 FROM t2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
c1
--
1
2
3
4The following picture illustrates the UNION operation of t1 and t2 tables:
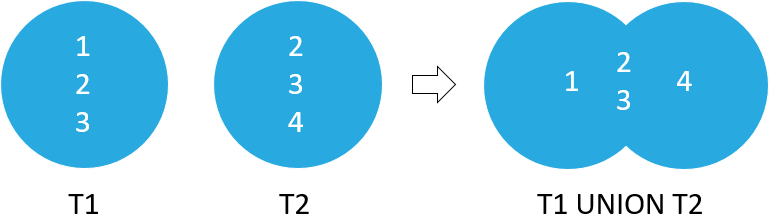
The following statement combines the result sets of t1 and t2 tables using the UNION ALL operator:
SELECT
c1
FROM
t1
UNION ALL
SELECT
c2
FROM
t2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
c1
--
1
2
3
2
3
4The following picture illustrates the UNION ALL operation of the result sets of t1 and t2 tables:
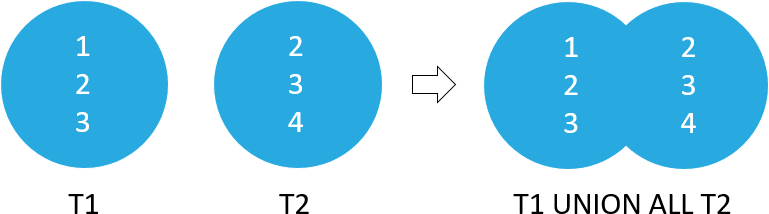
SQLite UNION operator examples
Let’s take some examples of using the UNION operator. We’ll use the employees and customers tables from the sample database.
1) Basic SQLite UNION operator example
This statement uses the UNION operator to combine the names of employees and customers into a single list:
SELECT
FirstName,
LastName,
'Employee' AS Type
FROM
employees
UNION
SELECT
FirstName,
LastName,
'Customer'
FROM
customers;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial output:
FirstName LastName Type
--------- ------------ --------
Aaron Mitchell Customer
Alexandre Rocha Customer
Andrew Adams Employee
Astrid Gruber Customer
Bjørn Hansen Customer
Camille Bernard Customer
...2) Using the UNION operator with ORDER BY example
This example uses the UNION operator to combine the names of the employees and customers into a single list. In addition, it uses the ORDER BY clause to sort the name list by first name and last name.
SELECT
FirstName,
LastName,
'Employee' AS Type
FROM
employees
UNION
SELECT
FirstName,
LastName,
'Customer'
FROM
customers
ORDER BY
FirstName,
LastName;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial output:
FirstName LastName Type
--------- ------------ --------
Aaron Mitchell Customer
Alexandre Rocha Customer
Andrew Adams Employee
Astrid Gruber Customer
Bjørn Hansen Customer
Camille Bernard Customer
Daan Peeters Customer
Dan Miller Customer
Diego Gutiérrez Customer
Dominique Lefebvre Customer
Eduardo Martins Customer
...Summary
- Use the
UNIONoperator to combine rows from two result sets into a single result set. - Use the
UNION ALLoperator to retain the duplicate rows in the final result set.
