| CARVIEW |
Overview
- Download Link
- Wireshark User Guide
Wireshark is a network packet analyzer. A network packet analyzer presents captured packet data in as much detail as possible. You could think of a network packet analyzer as a measuring device for examining what’s happening inside a network cable, just like an electrician uses a voltmeter for examining what’s happening inside an electric cable (but at a higher level, of course).
Tutorial
Wireshark for WiFi
Wireshark for IEEE 802.15.4
Wireshark for Bluetooth
Wireshark for LoRaWAN
]]>Overview
Machine Learning
- Python Machine Learning Tutorial, Scikit-Learn
- Training Support Vector Machines for Multiclass Classification
Deep Learning Tutorials
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
What is Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
- A Comprehensive Guide to Convolutional Neural Networks
- Matlab, Explanation of Different Layers of Convolutional Neural Networks
CNN Examples
- Building a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in Keras
- Your First Deep Learning Project in Python with Keras Step-By-Step
- How to Develop 1D Convolutional Neural Network Models for Human Activity Recognition
Common CNN Architecture
- Illustrated: 10 CNN Architectures: LeNet-5, AlexNet, VGG-16, Inception-v1, Inception-v3, ResNet-50, Xception, Inception-v4, Inception-ResNets, ResNeXt-50
AlexNet
Few Shot Learning
- An Introduction to Few-Shot Learning
- Understanding Few-Shot Learning in Computer Vision – What You Need to Know
Development Tool
Python
I strongly recommend installing Anaconda Distribution.
Keras
Matlab
Code Snippet
- Check the installed packages
conda list - Install a particular tensorflow version using conda
conda install -c conda-forge tensorflow=1.13
Online Resources
- CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition at Stanford University link
- A summary of resources link
- Book Dive into Deep Learning
Overview
There is some confusion about the Bluetooth. Generally speaking, Bluetooth 1.0 - 3.0 includes classic Bluetooth. Bluetooth 4.0 starts to use Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). A brief introduction about their difference can be found at link1, link2 and link3.
New features of Bluetooth 5 can be found here. The full and latest specification, v5.2 (released in 2019) can be downloaded here.
Unless otherwise highlighted, the following descriptions apply to BLE, which might not be correct for classic Bluetooth.
Network Architecture
- Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint Connection Topology (Both Bluetooth classic and BLE)
- Broadcast Connection Topology (BLE only)
- Mesh Connection Topology (BLE only)
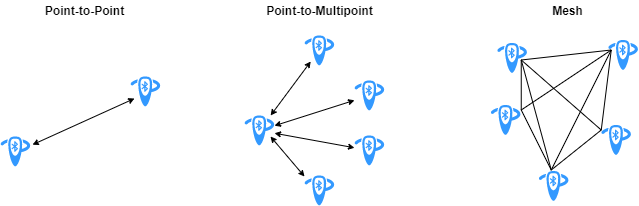
Figure from https://uk.mathworks.com/help/comm/ug/bluetooth-mesh-networking.html.
Protocol Overview
Visit MATLAB Bluetooth Protocol Stack for a detailed introduction about the Bluetooth and BLE protocol, and a mapping between them and the OSI model.
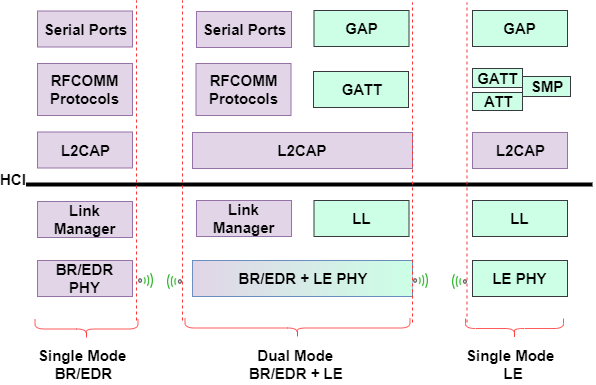
Figure from https://uk.mathworks.com/help/comm/ug/bluetooth-protocol-stack.html.
Some brief introduction of the protocol can be found at the Microchip Developer Center. The BLE protocol stack consists of
- Controller (Physical Layer and Link Layer)
- Host
- Application
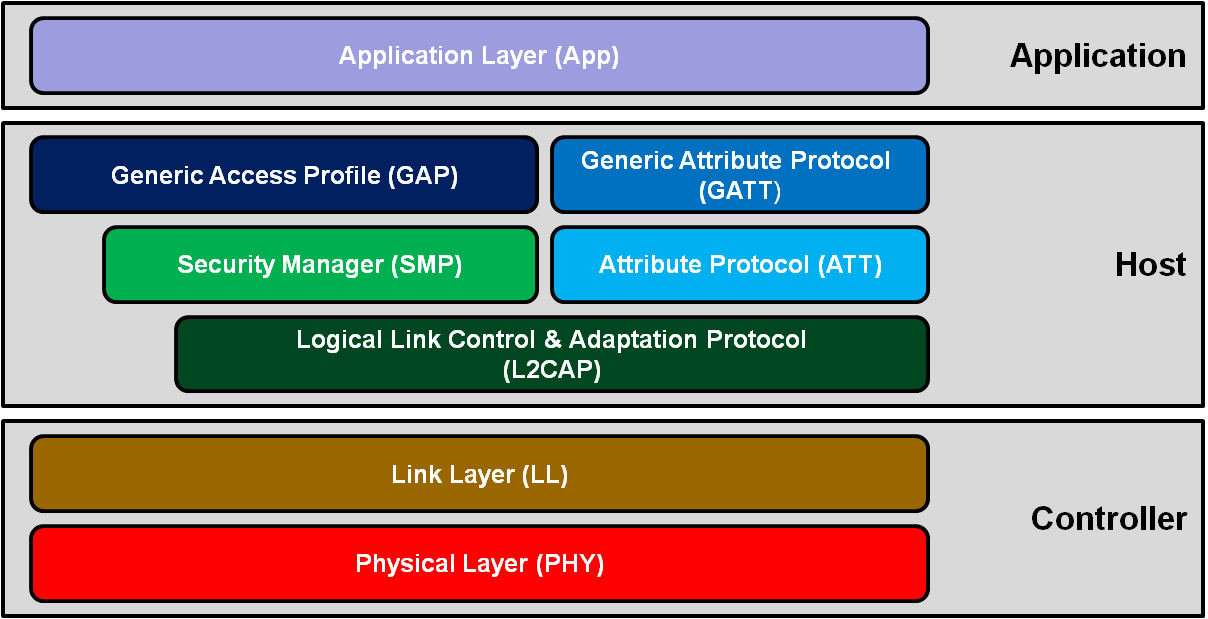
Figure from https://microchipdeveloper.com/wireless:ble-introduction.
Physical Layer
Some key features of the BLE physical layer
- 2.4GHz ISM band. The band between 2.402 GHz to 2.4835 GHz is divided into 40 channels with 2 MHz channel spacing, $f_k = 2402 + k*2 MHz, k = 0, 1, …, 39$
- The 40 channels are divided into advertising channels (Ch. 37, 38, and 39) and 37 data channels (Ch. 0-36).
- Gaussian Frequency-Shift Keying (GFSK).
- Adaptive Frequency Hopping for data channels. The channel selection algorithms can be found in Section 4.5.8 of Part B vol. 6. There are two algorithms defined and the algorithm#1 selects the channel as $f_{n+1} = (f_n + hop)$ mod 37, where hop ranges from 5-16.
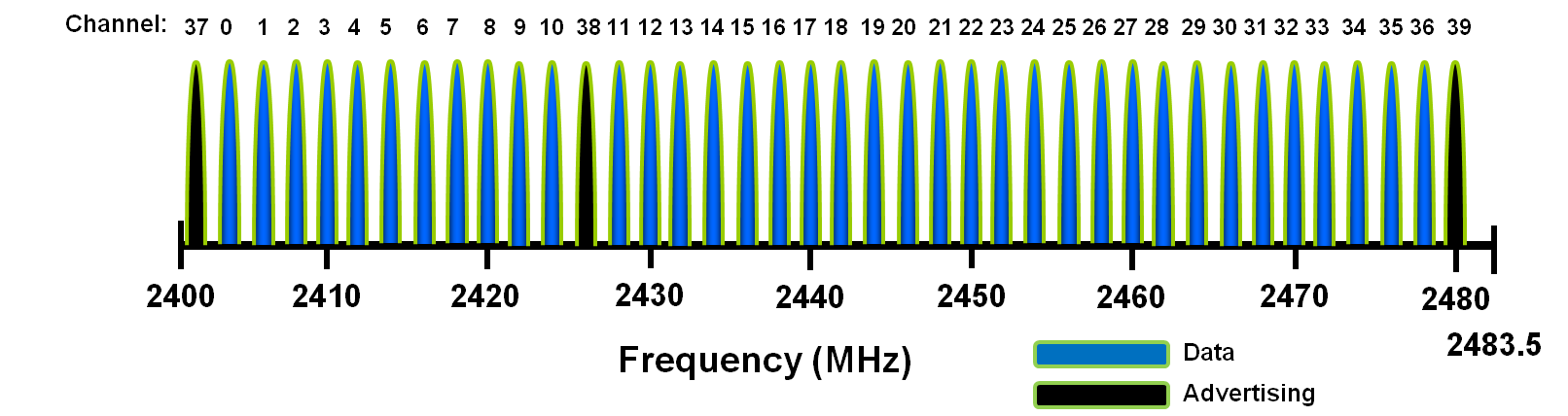
Figure from https://microchipdeveloper.com/wireless:ble-introduction.
Preamble
The preamble defined in BLE v5.2:
- LE IM packets (8 bits): 10101101, or 01010101
- LE 2M packets (16 bits): 1010110110101101, or 0101010101010101 Preamble is used for frequency synchronization, symbol timing and automatic gain control. Visit Page 2865 Section 2.1.1 Vol 6, Part B of the Bluetooth Core Specification v5.2.
Link Layer
- Advertising and Scanning
- Connection
- Network Topology - Piconet
- Security - AES - CCM
Advertising Channel
Channel 37, 38 and 39
- Device Discovery
- Connection Establishment
- Broadcast Transmissions
Data Channel
Channel 0-36
- Data transmissions
- Frequency hopping is used to select different channels.
Packet Type
The same packet format for both
- Advertising channel packets
- Data channel packets
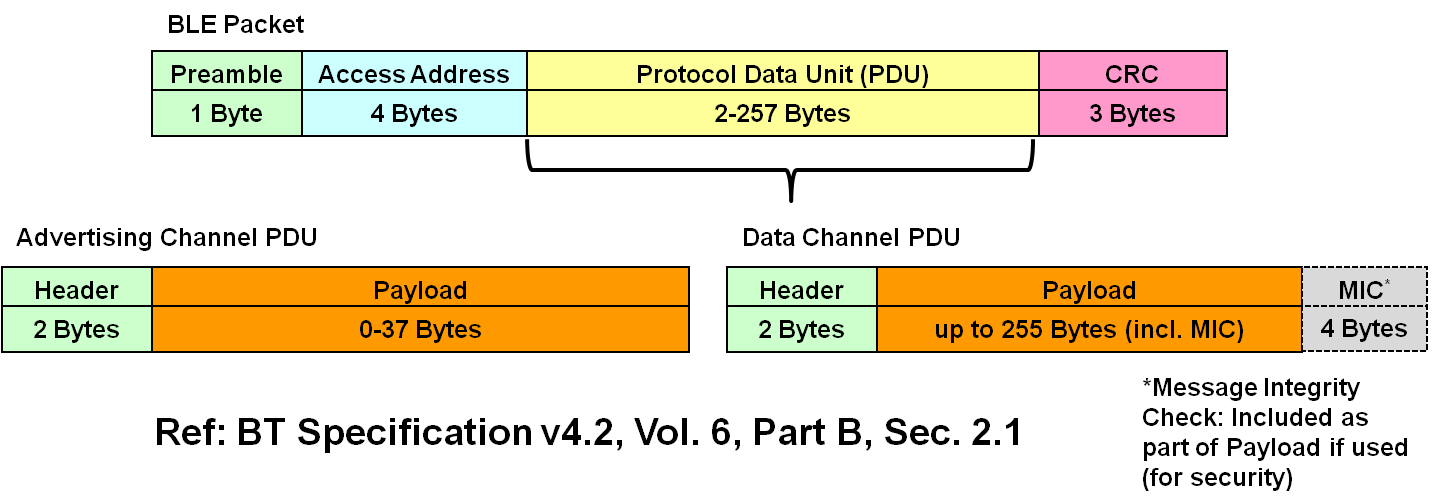
BLE Packet Type. Figure from https://microchipdeveloper.com/wireless:ble-link-layer-packet-types
Discovery Process
- Advertising interval: 20 ms
- Scan interval: 50 ms
- Scan window: 25 ms
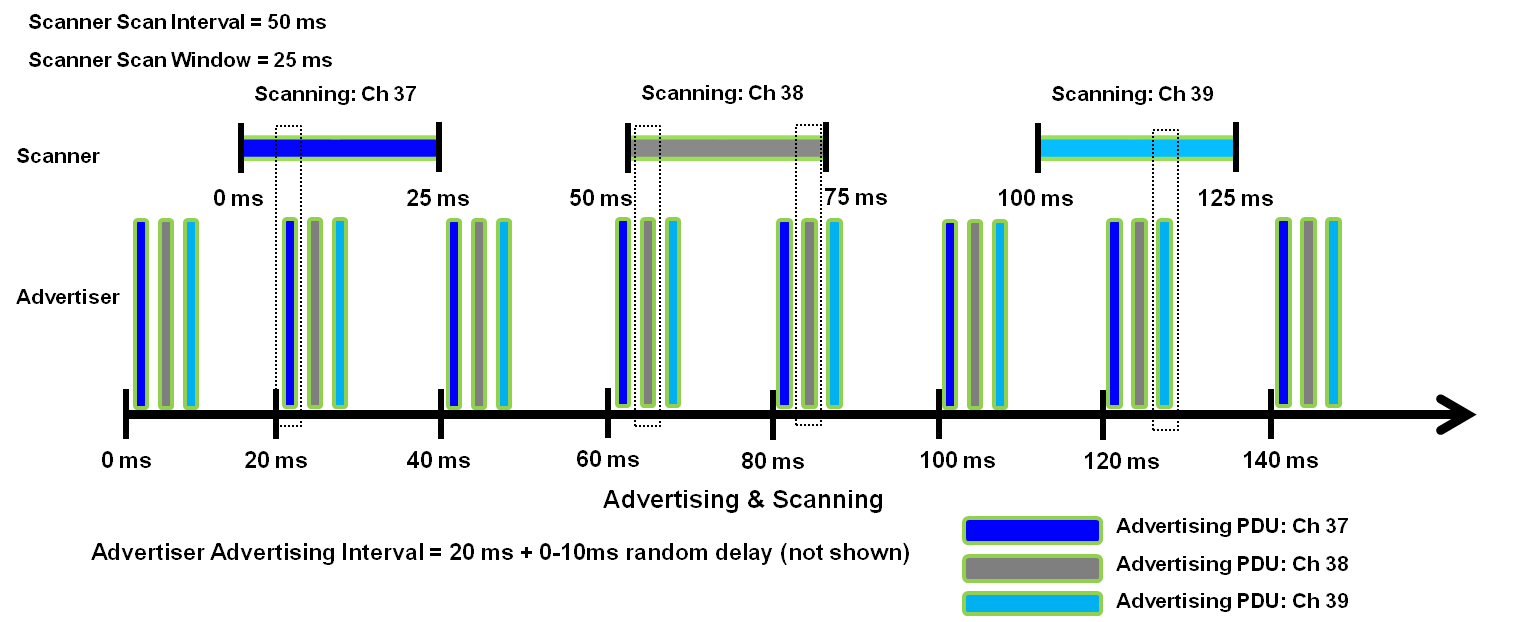
Advertising and Scanning. Figure from https://microchipdeveloper.com/wireless:ble-link-layer-discovery
Connection Process
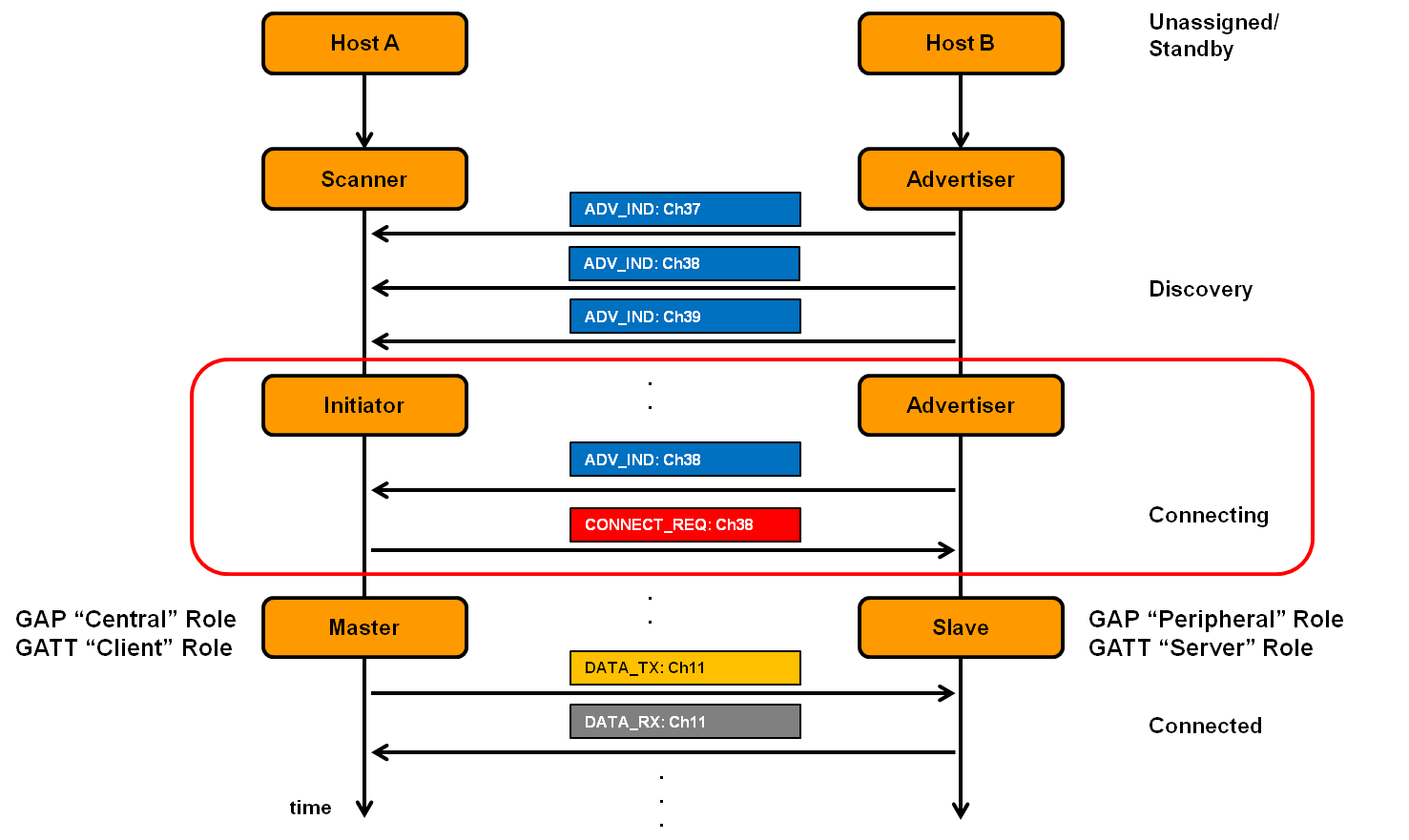
Connection establishment. Figure from https://microchipdeveloper.com/wireless:ble-link-layer-connections
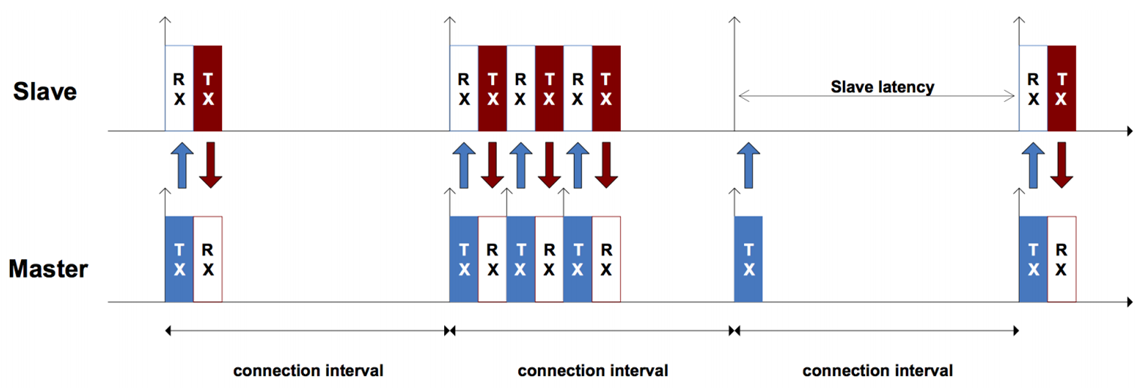
Connected phase. Figure from https://microchipdeveloper.com/wireless:ble-link-layer-connections
Bluetooth Stack and Development Kit
Linux
- C language: BlueZ. Check An Introduction to Bluetooth Programming about its usage.
- Python: bluepy.
Micropython
Note: The module is still under development and its classes, functions, methods and constants are subject to change. It only supports the basic BLE functions.
Texas Instruments
- TI BLE SDK support Bluetooth 4.2 and Bluetooth 5.
- TI BLE-Stack for Bluetooth 4.2 API Documentation 3.01.00.07
- SimpleLink™ CC26x2 SDK BLE5-Stack User’s Guide.
- SimpleLink™ CC13x2 / CC26x2 SDK BLE5-Stack User’s Guide.
- Supported TI devices can be found here.
Scapy for Bluetooth
Matlab Bluetooth Support
Matlab has also provided simulation support for Bluetooth and BLE. Visit Communications Toolbox Library for the Bluetooth Protocol support package for more information.
]]>Overview
IEEE 802.15.4 defines the physical and MAC layers. ZigBee is based on IEEE 802.15.4 but also defines higher layer protocols.
IEEE 802.15.4 is also adopted by 6LoWPAN, WirelessHART, THREAD, etc.
IEEE 802.15.4
Physical Layer
Frequency Band
- 868 MHz, Europe, channel $k$ = 0, $f_c = 868.3$ MHz
- 915 MHz, America, Australia, channel $k=$ 1 - 10, $f_c = 906 + 2(k-1)$ MHz
- 2.4 GHz, Worldwide, channel $k$ = 11 - 26, $f_c = 2405 + 5*(k-11)$ MHz, OQPSK
OQPSK PHY

Figure from https://uk.mathworks.com/help/comm/ug/end-to-end-ieee-802-15-4-phy-simulation.html.
All OQPSK PHYs map every 4 PPDU bits to one symbol. The 2.4 GHz OQPSK PHY spreads each symbol to a 32-chip sequence, while the other OQPSK PHYs spread it to a 16-chip sequence. Then, the chip sequences are OQPSK modulated and passed to a half-sine pulse shaping filter (or a normal raised cosine filter, in the 780 MHz band).
Run the Matlab End-to-End IEEE 802.15.4 PHY Simulation to have a deep understanding on the modulation.
Please refer to Section 1.1.1.2 O-QPSK PHY of the Rohde & Schwarz Application Note for a detailed introduction.
MAC Layer
CSMA-CA
- Direct Transmission
- Indirect Transmission (Polling)
MAC Type
- Data Frame
- Beacon Frame
- Acknowledgement Frame
- MAC Command Frame
ZigBee
Network Architecture and Topology
- Star Topology
- Tree Topology
- Mesh Topology
Tutorial
Check the first chapter of IEEE 802.15.4 Stack User Guide for a brief introduction of IEEE 802.15.4.
]]>Overview
Linux Test
How To Start
- If you are using Windows OS, you can access to the remote server by
- Putty
- MobaXterms (recommended)
- How to configure Putty & Xming (on your laptop) from University of California, Irvine
- Basic Commands
cd,ls,mkdir,pwd,cat,grep,sudo
Common Usage
- Ubuntu Documentation on How to Use the Terminal
- Graphic Notebook Editor
- Command:
gedit file_name.extension
- Command:
vimgetting started- Display information of your active processes.
- Command:
ps -ef | grep loginnameOrps -ef | grep first_7_characters_of_your_loginname_if_it_is_longer_than_8_characters
- Command:
- Kill A Process
- Command:
kill PID
- Command:
-
Copy all the contents of ~/folder1 to ~/new_folder1:
cp -r ~/folder1/. ~/new_folder1 - Module
- Check available modules:
module avail - Check loaded modules:
module list - Load a module:
module load apps/MATLAB/R2020a - Unload a module:
module unload apps/MATLAB/R2020a
- Check available modules:
Running Matlab Remotely in a Server
Step 1: Load Matlab
- Command:
module load apps/MATLAB/R2020a
Step 2: Run Matlab without GUI and in the background
- Command:
nohup matlab -r MatlabScriptName -nodisplay - nosplash -nojvm -nodesktop &
The above command may output Bad file descriptor and Warning: “Error reading Character from command line” error. In this case, using the following command instead:
nohup matlab -nodesktop -nosplash -nodisplay < main.m >log.txt 2>&1 &
Explanation: https://www.programmersought.com/article/91451058498/
“>log.txt” refers to redirecting the output to log.txt. 2>&1 means to input the error information into log.txt, 2 Refers to the standard input and output error (stderr), 1 refers to the standard output (stdout), 2> & 1 means 2 is equivalent to 1 output, the last & is the meaning of background operation, combined with the nohup command.
Tutorial:
- How to run Matlab on server, University of Calgary
- How do I run my program in the background (including the use of ‘screen’)?, University of California, Berkeley
General Topics
- Pulse-Shape Filtering in Communications Systems, National Instruments Tutorial, link
- I/Q Data: Plain and Simple, National Instruments Tutorial, link
- PySDR: A Guide to SDR and DSP using Python, Online Book, link
OFDM
Recommended Book
Communications Textbook
]]>Overview
Getting Started
Step 1: Hardware and Software Setup
Getting Started with the LimeSDR
- Hardware assembly: https://wiki.myriadrf.org/LimeSDR_Hardware_Installation
- LimeSDR Windows Driver Installation
- Installing Lime Suite on Windows This completes the hardware and software setup.
Step 2: LimeSDR-USB Quick Test
Tutorial
- LimeSDR Made Simple. The webpage does not give a full list of the tutorial series, google search “LimeSDR Made Simple”
Strictly speaking, IEEE 802.11 is the standard by IEEE and WiFi is a trademark of the WiFi alliance. However, they are used interchangably in this post.
Standard
IEEE 802.11 standard defines the physcai layer and media access control (MAC) layer protocols. It has undergone a number of amendments in the last twenty years, since its first release in 1997. A complete list of the IEEE 802.11 amendments is summarized at wikipedia.
PHY Layer
The main physical layer amendments include 802.11b (1999, DSSS), 802.11a (1999, OFDM, 5 GHz), 802.11g (2003, OFDM, 2.4 GHz), 802.11n (2009, MIMO OFDM, high throughput), 802.11ac (2013, MIMO OFDM, very high throughput), 802.11 ax(est late 2019, high efficiency).
OFDM Basics
IEEE 802.11 OFDM Receiver Design
- Check this paper Performance Assessment of IEEE 802.11p with an Open Source SDR-Based Prototype for the receiver design, including time synchronization, frequency offest estimation, channel estimation, etc.
MAC Layer
WiFi use CSMA/CA as the MAC layer protocol.
Frame Types
- Control frames
- Management frames
- Data frames
How 802.11 Wireless Works 802.11 Association Process Explained
802.11 Wi-Fi Connection/Disconnection process
802.11 Wi-Fi Security Concepts
Testbed and Implementations
The commercial network interface cards (NICs) only provide received signal strength indicator (RSSI) but not channel state information (CSI). RSSI represents the received power which is averaged over a packet, thus it is a coarse grained parameter. On the other hand, CSI is a fine grained parameter, and offers detailed channel response over different frequencies/subcarriers, when OFDM-based technique is used. Since CSI is much more useful for innovative research, a (incomplete) list of testbed is given below.
USRP Software Defined Radio (USRP)
- https://www.wime-project.net/
- IEEE 802.11 a/g/p transceiver for GNU Radio
Openwifi
- openwifi is an SDR (Software Defined Radio) implementation for IEEE802.11/Wi-Fi design with Linux mac80211 compatible full-stack.
- zynq FPGA + FMCOMMS2/3/4 RF board
- For Chinese user, there is a presentation video introducing openwifi by Dr. Jiao.
WARP 802.11 Reference Design
There is an 802.11 reference design implemented for WARP boards, which is compatible with the commercial WiFi. An experimental framework is implemented by Python for the research development. The available variables/parameters can be found here, among which the CSI is made public.
WARP is being actively used for research in many areas like power management, architectures for wireless receivers, physical layer algorithms, access protocols, routing and cognitive radios.
A list of papers using WARP can be found at here.
Network Interface Cards
Intel 5300 NIC
There is the Linux 802.11n CSI Tool for Intel 5300 NIC. This Intel NIC together with the CSI tool have been used extensively by researchers and led to many excellent research papers. A list of the relevant publications can be found at link.
Please note PCI-e interface is required for these NICs.
Atheros Chipsets
There is Atheros CSI Tool. A list of the relevant publications can be found at here.
Braodcom WiFi Chipsets
Software Tool
Matlab WLAN Toolbox
The Matlab WLAN Toolbox is very powerful. There are many useful functions and examples. Both PHY and MAC layers are supported. I strongly suggest to test your idea and algorithms using this Toolbox before you do it with real hardware.
Scapy
Scapy official website defines
Scapy is a Python program that enables the user to send, sniff and dissect and forge network packets. This capability allows construction of tools that can probe, scan or attack networks.
There is a library supporting IEEE 802.11.
Code Examples:
- PythonScapyDot11_TheBook
- Fake a WLAN connection via Scapy
- Generating WiFi communication in Scapy tool CWAP 802.11- Probe Request/Response
- WiFi Karma: A Brief Guide On Probe Response Frames
Radiotap
- What is radiotap? link
Network Monitoring
Misc Resources
Wireshark
- Download Link
- Wireshark User Guide
Wireshark is a network packet analyzer. A network packet analyzer presents captured packet data in as much detail as possible. You could think of a network packet analyzer as a measuring device for examining what’s happening inside a network cable, just like an electrician uses a voltmeter for examining what’s happening inside an electric cable (but at a higher level, of course).
WiFi Modes
]]>Set the operating mode of the device, which depends on the network topology. The mode can be Ad-Hoc (network composed of only one cell and without Access Point), Managed (node connects to a network composed of many Access Points, with roaming), Master (the node is the synchronisation master or acts as an Access Point), Repeater (the node forwards packets between other wireless nodes), Secondary (the node acts as a backup master/repeater), Monitor (the node is not associated with any cell and passively monitor all packets on the frequency) or Auto.
Overview
Lego Robot
Micropython Development
]]>How to Write a Paper
Information for Authors
Each journal and conference will have information for authors, which will explain the requirements in terms of the number of pages, format, resubmission, page overlength charge, etc.
For example, the information for authors of IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications can be found here.
Template
Each journal and conference will usually have both Word and Latex templates. When possible, the Latex templates are always recommended. Please read this post for How to Use LaTex.
Please note that IEEE journals will have different templates. Download your right template from here.
Extending Conference Paper to Journal
There may be different rules for journals regarding extending a conference paper. Please refer to the website of the particular journal for detailed instruction.
For example, the policy of IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications can be found here.
How to Write a Good Paper
Tips
- Common Bugs in Writing
- Top-10 tips for writing a paper by Jim Kurose, University of Massachusetts
- Tips about writing systems papers by Prof Lin Zhong, Yale University
- How to write for Technical Periodicals & conferences by IEEE
Making Your Article interesting to Read
- Write in paragraphs, not long blocks of text [12]. every paragraph should have a topic sentence, supporting sentences that build on that key message, and a summary sentence. Vary the length of your paragraphs to make your article easier to read. Think about the transition from one paragraph to the next. is there a logical progression?
- Write clear, simple sentences in the form of noun-verb-object. Varying sentence length can make an article more engaging. compound sentences add variety and are useful for comparing ideas [12]. every word in a sentence should contribute something; eliminate unnecessary words.
- avoid the passive voice, in which the subject is acted upon. in the active voice, the subject performs the action. “it was hypothesized,” is passive; “We hypothesized,” is active. The active voice is more interesting and less ambiguous. edit passive sentences to active sentences as much as possible.
- Write in the first person (“i,” “we”) to make it clear who has done the work and the writing. it is particularly helpful when you are comparing your work to someone else’s work [3].
- The abstract and the methods section will be written in the past tense, because they describe work that you have already done. The introduction and discussion section are usually written in the present tense, because they describe knowledge that currently exists.
Abstract and Title
Some suggestions from the Information for Authors IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence Author Instructions Title
Avoid phrases such as “a novel methodology”, “a new algorithm”, and “a significant application” in the title. By default, papers in TAI offer novel contributions that are significant. One purpose of the paper is to convince the reader that the contribution is novel, scientifically sound, technically correct, and significant. As such, words such as ‘novel’ and ‘new’ are redundant.
Abstract
The “Abstract” should not exceed 250 words. Authors are encouraged to attempt to use the following guideline in writing their abstract:
- 1-2 sentences introducing the problem.
- 2-3 sentences summarizing the state-of-art. Be concise and offer an objective assessment of the current state of play in this area.
- 1-2 sentences clearly describing the research gap the paper is concerned with.
- 1-2 sentences summarizing the main methodological contribution.
- 1-2 sentences summarizing the main result.
- 2-3 sentences summarizing the implications of the findings on the wider field of AI.
