Reading and Writing JSON to a File in Python
Last Updated :
14 Jul, 2025
The full form of JSON is Javascript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called JSON. To use this feature, we import the JSON package in Python script. The text in JSON is done through quoted-string which contains the value in key-value mapping within {}. It is similar to the dictionary in Python.
Writing JSON to a file in Python
Serializing JSON refers to the transformation of data into a series of bytes (hence serial) to be stored or transmitted across a network. To handle the data flow in a file, the JSON library in Python uses dump() or dumps() function to convert the Python objects into their respective JSON object, so it makes it easy to write data to files. See the following table given below.
| PYTHON OBJECT | JSON OBJECT |
|---|
| Dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str | string |
| int, long, float | numbers |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
Let's explore two methods to write a JSON file in Python.
Using json.dumps()
The JSON package in Python has a function called json.dumps() that helps in converting a dictionary to a JSON object. It takes two parameters:
- dictionary: the name of a dictionary which should be converted to a JSON object.
- indent: defines the number of units for indentation
After converting the dictionary to a JSON object, simply write it to a file using the "write" function.
Python
import json
dictionary = {
"name": "sathiyajith",
"rollno": 56,
"cgpa": 8.6,
"phonenumber": "9976770500"
}
# Serializing json
json_object = json.dumps(dictionary, indent=4)
# Writing to sample.json
with open("sample.json", "w") as outfile:
outfile.write(json_object)
Output:
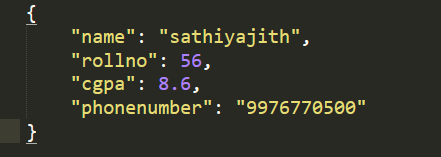 Output using json.dumps()
Output using json.dumps()Using json.dump()
Another way of writing JSON to a file is by using json.dump() method. The JSON package has "dump" function which directly writes the dictionary to a file in the form of JSON, without needing to convert it into an actual JSON object. It takes 2 parameters:
- dictionary - the name of a dictionary which should be converted to a JSON object.
- file pointer - pointer of the file opened in write or append mode.
Python
# Python program to write JSON
# to a file
import json
# Data to be written
dictionary = {
"name": "sathiyajith",
"rollno": 56,
"cgpa": 8.6,
"phonenumber": "9976770500"
}
with open("sample.json", "w") as outfile:
json.dump(dictionary, outfile)
Output
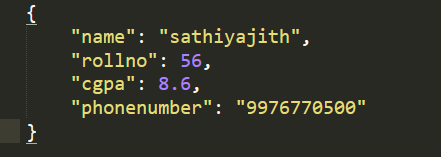 Output using json.dump()
Output using json.dump()Reading JSON from a file using Python
Deserialization is the opposite of Serialization, i.e. conversion of JSON objects into their respective Python objects. The load() method is used for it. If you have used JSON data from another program or obtained it as a string format of JSON, then it can easily be deserialized with load(), which is usually used to load from a string, otherwise, the root object is in a list or Dict.
Let's explore two methods to Read JSON file in Python.
Using json.load()
The JSON package has json.load() function that loads the JSON content from a JSON file into a dictionary. It takes one parameter:
File pointer: A file pointer that points to a JSON file.
Python
import json
with open('sample.json', 'r') as openfile:
json_object = json.load(openfile)
print(json_object)
print(type(json_object))
Output:
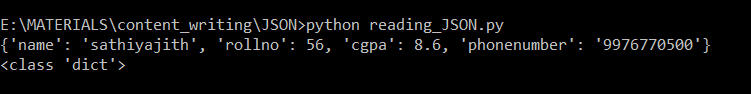 Output using json.load()
Output using json.load()Using json.loads()
json.loads() function is used to parse a JSON string and convert it into a Python object. It takes one parameter:
JSON string: A valid JSON-formatted string.
Python
import json
json_string = '{"name": "Francis", "age": 25, "city": "New York"}'
# Convert JSON string to Python dictionary
json_object = json.loads(json_string)
print(json_object)
print(type(json_object))
 Output using json.loads()
Output using json.loads()Related articles:
Reading and Writing JSON to a File in Python
