Saving Text, JSON, and CSV to a File in Python
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
Python allows users to handle files (read, write, save and delete files and many more). Because of Python, it is very easy for us to save multiple file formats. Python has in-built functions to save multiple file formats.
Opening a text file in Python
Opening a file refers to getting the file ready either for reading or for writing. This can be done using the
open() function.
Syntax:
File_object = open("File_Name", "Access_Mode")
Parameters:
- File_Name: The name of the file that is needed to be opened.
- Access_Mode: Access modes govern the type of operations possible in the opened file.
Following are the most commonly used access modes:
- Read Only (‘r’): Open text file for reading.
- Write Only (‘w’): Open the file for writing.
- Append Only (‘a’): Open the file for writing. The data being written will be inserted at the end, after the existing data.
- Read and Write (‘r+’): Open the file for reading and writing.
Note: By default, Python assumes the access mode as read i.e ("r")
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# opening a file
# Open function to open the file "myfile.txt"
# (same directory) in read mode and store
# it's reference in the variable file1
file1 = open("myfile.txt")
# Reading from file
print(file1.read())
file1.close()
For more information, refer to
Open a File in Python.
Saving a Text File in Python
After learning about opening a File in Python, let's see the ways to save it. Opening a new file in write mode will create a file and after closing the file, the files get saved automatically. However, we can also write some text to the file. Python provides two methods for the same.
Example:
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# saving a text file
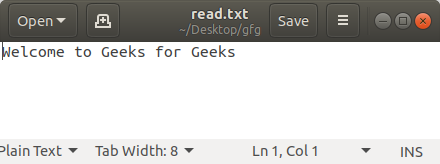
file = open('read.txt', 'w')
file.write('Welcome to Geeks for Geeks')
file.close()
With Statement
with statement in Python is used in exception handling to make the code cleaner and much more readable. It simplifies the management of common resources like file streams. Unlike the above implementations, there is no need to call
file.close() when using
with statement. The
with statement itself ensures proper acquisition and release of resources.
Syntax:
with open filename as file:
statement(s)
Example:
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# saving a text file
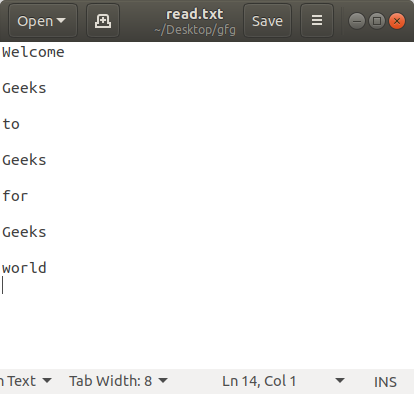
with open('read.txt', 'w') as file:
books = ['Welcome\n',
'Geeks\n',
'to\n',
'Geeks\n',
'for\n',
'Geeks\n',
'world\n']
file.writelines("% s\n" % data for data in books)
 Note:
Note: For more information, refer to
Writing to file in Python.
Saving a CSV File in Python
CSV is a Comma Separated Values files are most widely utilized for putting tabular data. CSV file stores tabular data (numbers and text) in plain text. Each line of the file is a data record. Each record consists of one or more fields, separated by commas. Python has built-in module called
csv to write and Save a CSV File.
To save a CSV File:
- First, we need to import csv library.
- Then open the file as we usually do but instead of writing content on the read_file object, we create a new object called read_writer.
- This object provides us with the writelines() method which allows us to place all the row's data within the enter one go.
Example:
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# writing to CSV
import csv
# field names
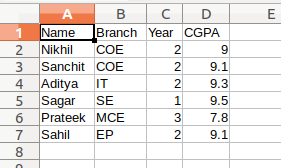
fields = ['Name', 'Branch', 'Year', 'CGPA']
# data rows of csv file
rows = [ ['Nikhil', 'COE', '2', '9.0'],
['Sanchit', 'COE', '2', '9.1'],
['Aditya', 'IT', '2', '9.3'],
['Sagar', 'SE', '1', '9.5'],
['Prateek', 'MCE', '3', '7.8'],
['Sahil', 'EP', '2', '9.1']]
# name of csv file
filename = "university_records.csv"
# writing to csv file
with open(filename, 'w') as csvfile:
# creating a csv writer object
csvwriter = csv.writer(csvfile)
# writing the fields
csvwriter.writerow(fields)
# writing the data rows
csvwriter.writerows(rows)
 Note:
Note: For more information, refer to
Writing CSV files in Python.
Saving a JSON File in Python
The full-form of JSON is JavaScript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called
json. The text in JSON is done through quoted-string which contains the value in key-value mapping within
{ }.
This module provides a method called
dump() which converts the Python objects into appropriate json objects.
Python3
import json
# python object(dictionary) to be dumped
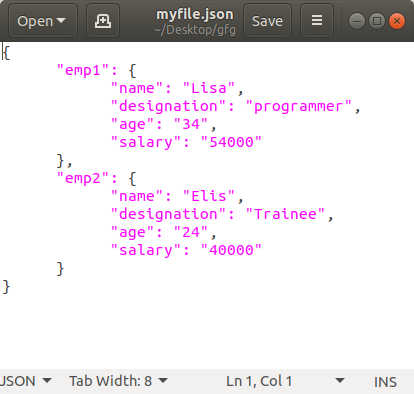
dict1 ={
"emp1": {
"name": "Lisa",
"designation": "programmer",
"age": "34",
"salary": "54000"
},
"emp2": {
"name": "Elis",
"designation": "Trainee",
"age": "24",
"salary": "40000"
},
}
# the json file where the output must be stored
out_file = open("myfile.json", "w")
json.dump(dict1, out_file, indent = 6)
out_file.close()
 Note:
Note: For more information, refer to
Working With JSON Data in Python.
