Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree in Python
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Inorder traversal is defined as a type of tree traversal technique which follows the Left-Root-Right pattern, such that:
- The left subtree is traversed first
- Then the root node for that subtree is traversed
- Finally, the right subtree is traversed
Consider the following tree:
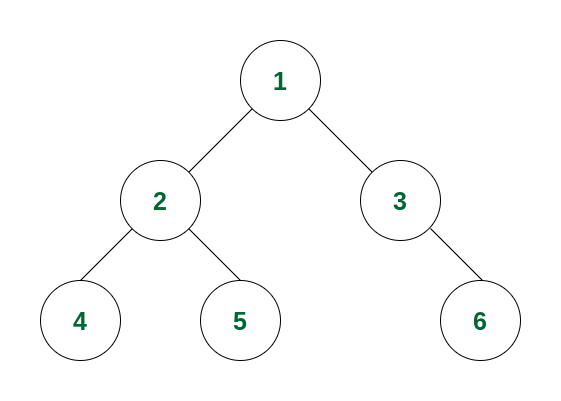
If we perform an inorder traversal in this binary tree, then the traversal will be as follows:
Step-by-step approach:
- Step 1: The traversal will go from 1 to its left subtree i.e., 2, then from 2 to its left subtree root, i.e., 4. Now 4 has no left subtree, so it will be visited. It also does not have any right subtree. So no more traversal from 4
- Step 2: As the left subtree of 2 is visited completely, now it read data of node 2 before moving to its right subtree.
- Step 3: Now the right subtree of 2 will be traversed i.e., move to node 5. For node 5 there is no left subtree, so it gets visited and after that, the traversal comes back because there is no right subtree of node 5.
- Step 4: As the left subtree of node 1 is, the root itself, i.e., node 1 will be visited.
- Step 5: Left subtree of node 1 and the node itself is visited. So now the right subtree of 1 will be traversed i.e., move to node 3. As node 3 has no left subtree so it gets visited.
- Step 6: The left subtree of node 3 and the node itself is visited. So traverse to the right subtree and visit node 6. Now the traversal ends as all the nodes are traversed.
So the order of traversal of nodes is 4 -> 2 -> 5 -> 1 -> 3 -> 6.
Examples of Inorder Traversal
Input:
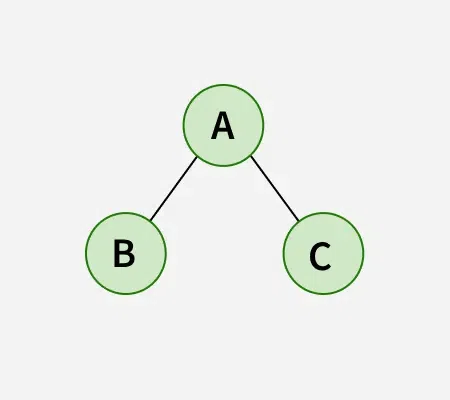
Output: BAC
Explanation: The Inorder Traversal visits the nodes in the following order: Left, Root, Right. Therefore, we visit the left node B, then the root node A and lastly the right node C.
Input :
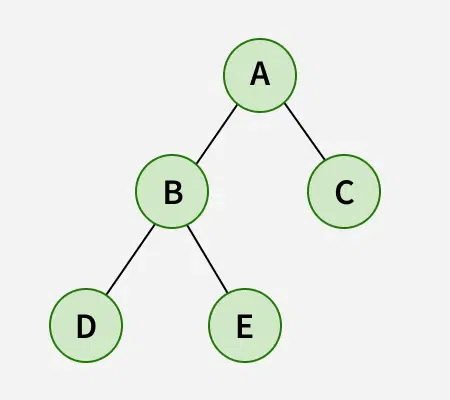
Output: DBEAC
Input: NULL
Output:
Output is empty in this case.
Algorithm for Inorder Traversal
Inorder(root):
- If root is NULL, then return
- Inorder (root -> left)
- Process root (For example, print root’s data)
- Inorder (root -> right)
Python Program to implement Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Python
# Structure of a Binary Tree Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, v):
self.data = v
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print inorder traversal
def printInorder(node):
if node is None:
return
# First recur on left subtree
printInorder(node.left)
# Now deal with the node
print(node.data, end=' ')
# Then recur on right subtree
printInorder(node.right)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.right = Node(6)
# Function call
print("Inorder traversal of binary tree is:")
printInorder(root)
OutputInorder traversal of binary tree is:
4 2 5 1 3 6
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the total number of nodes. Because it traverses all the nodes at least once.
Auxiliary Space: O(h) where h is the height of the tree. This space is required for recursion calls.
- In the worst case, h can be the same as N (when the tree is a skewed tree)
- In the best case, h can be the same as log N (when the tree is a complete tree
Related Posts:
