Gradle Tasks and Lifecycle
Last Updated :
28 Jul, 2025
Gradle is a powerful build automation tool which is used in software development, this tool not only run the tasks but it also manages the entire build process including dependencies and custom tasks. Understanding gradle and lifecycle concepts is important for developers who want to use it efficiently.
What are Gradle Tasks?
A Gradle task is a single job in the build process. It could be any task like compiling code, running tests, creating a package, or uploading files. These tasks are defined in a build script (build.gradle). Each task is a container for some action that needs to be performed, such as:
- Compiling a source code.
- Creating WAR and JAR files.
- Running unit test.
- Deploying applications
Gradle Task Lifecycle
Gradle arranges all the tasks in a specified sequence to make sure that they run properly. The build lifecycle tells about the stages the gradle build goes through and these stages are listed below:
Lifecycle Diagram
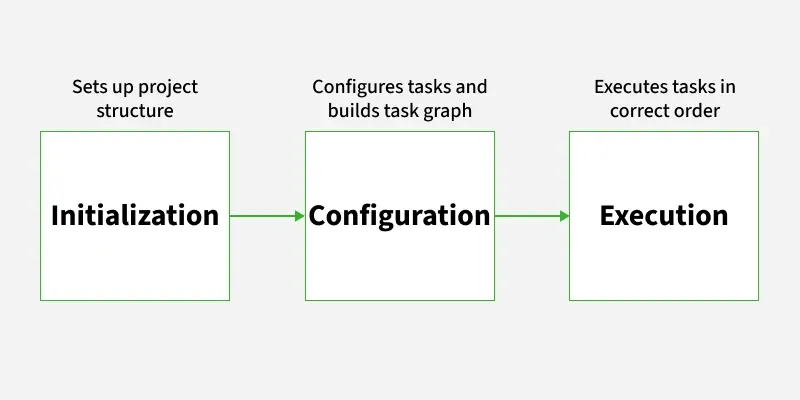 gradle-life-cycle
gradle-life-cycle1. Initialization Phase
This is the first stage and in this, the gradle finds out which projects are part of the build, and it only sets the project structure but it does not run any tasks.
2. Configuration Phase
This is the second stage and in this, the gradle sets up the project and prepares all the tasks that will be run later. No tasks are actually run yet. In this stage it is making everything ready only.
3. Execution Phase
This is the third stage and in this, all the tasks actually run based on the commands we pass to gradle. Gradle determines which tasks to execute and in what order. If dependencies exist between tasks, Gradle takes care of executing them in the correct order.
Now let's discuss about, the types of gradle tasks in more detail for better understanding
Types of Gradle Tasks
Gradle provides two main types of tasks which are listed below:
1. Built-In Tasks: Built-In Tasks are tasks that come pre-configured with gradle. Common built-in tasks include:
- build: It compiles and assembles the project.
- clean: It deletes the build directory.
- test: It runs unit tests for the project.
- jar: It creates a JAR file from the compiled classes.
Note: These tasks are part of the default Gradle plugin and are available in any Gradle project.
2. Custom Tasks: Custom tasks are tasks that we define in our build.gradle file. We can create a task to automate any action that Gradle does not handle by default.
Example 1:
Java
task helloWorld {
doLast {
println 'Welcome to the homePath'
}
}
output: This task will print a message when you run:
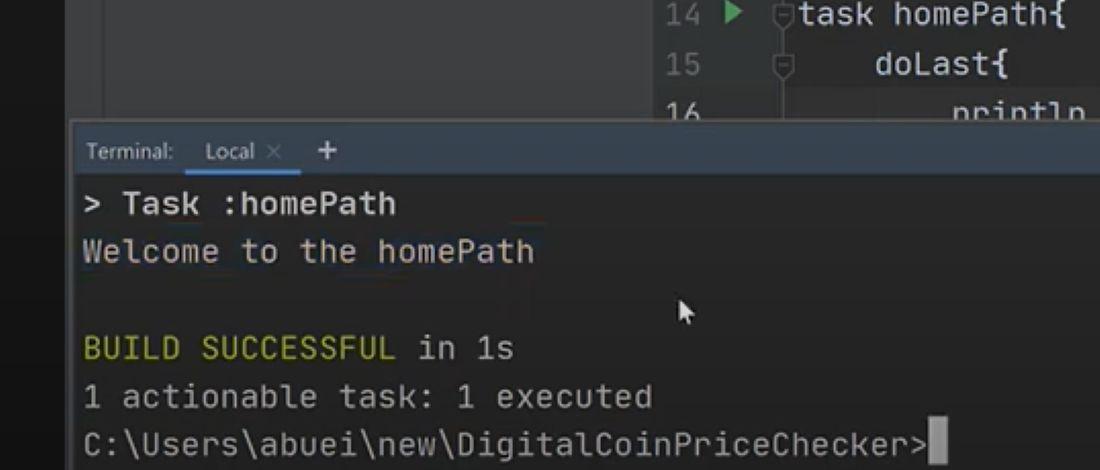 output
outputNote: In the above example, we have defined a custom task helloWorld and the doLast block defines the action that will be executed when the task is run.
Let's now understand how to create and configure tasks in gradle.
Creating and configuring tasks in Gradle is very straightforward. We can define tasks using the task keyword in our build.gradle file.
Example:
Java
task greet {
doLast {
println 'Hello from Gradle!'
}
}
Note: This code will simply prints "Hello from Gradle!". The doLast block is used to define the action to be taken when the task is executed. We can also use doFirst to specify actions to be executed before any other actions in the task.
Connecting Tasks (Task Dependencies)
What if you want one task to run before another? You can do that using dependsOn.
Example:
Java
task taskA {
doLast {
println 'Running Task A'
}
}
task taskB(dependsOn: taskA) {
doLast {
println 'Running Task B'
}
}
output:
gradle taskB
