| CARVIEW |
- CCNA online course
- Linux online course
- VMware ESXi online course
- Nmap online course
- MySQL online course
- Raspberry Pi online course
- Apache HTTP Server course
- VMware Player online course
- Splunk online course
- SQL online course
- Oracle VirtualBox online course
- Python online course
- Asterisk course
- VMware Workstation Player course
- Process Explorer course
- Pillow online course
- Create a web crawler in Python
- A short introduction to…
IDLE editor
The Python IDLE (Integrated DeveLopment Environment) editor is a graphical user interface for Python development. This GUI is free and installed automatically during the Python installation. It enables you to edit, run, and debug Python programs in a simple GUI environment.
IDLE is actually a Python program that uses the standard library’s tkinter GUI toolkit to build its windows. It is portable and can be run on all major platforms, such as Windows, Linux, Mac OS, etc. It supports the following features:
- command history and syntax colorization
- auto-indent and unindent for Python code
- word auto-completion
- support for multiple windows
- integrated debugger
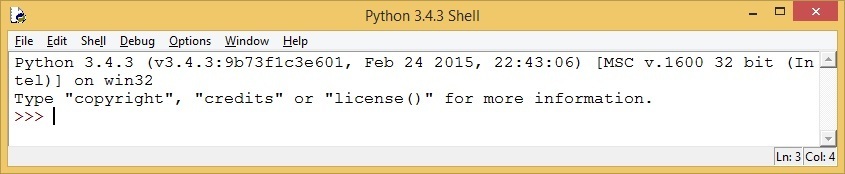
The Python IDLE is usually present as an entry in the Start button menu in Windows 7. In Windows 8 and higher versions, you can start it by typing IDLE from the Start menu. Once started, it will display some useful information about the Python version and the operating system:
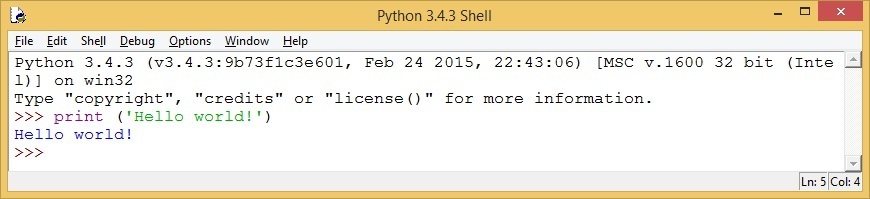
You can write your code after the >>> prompt and it will be executed when you press Enter:
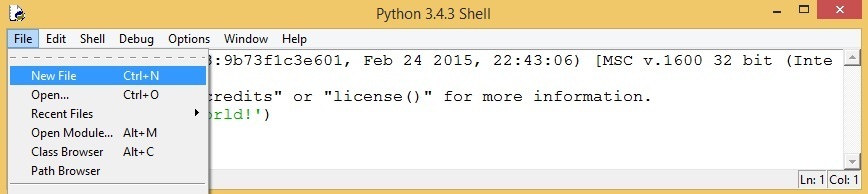
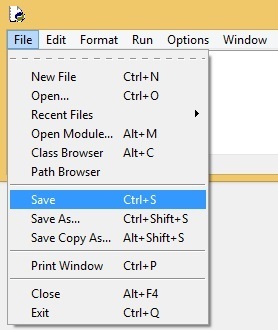
Although the shell window is useful for executing one-line commands, you will not use it to write full-fledged programs. Instead, Python IDLE comes with its own built-in text editor that you can use to write and save your code. You can start the editor by selecting File > New File:
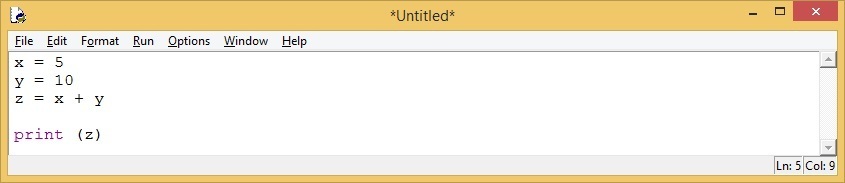
This opens up a window where you can type your code:
Before running your code, you will need to save it in a file (File > Save). Make sure that the file has the .py extension:
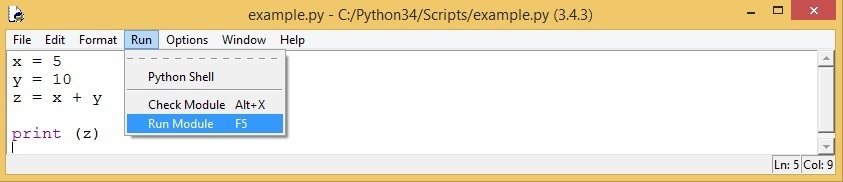
To run your code, click Run > Run Module (or press F5):
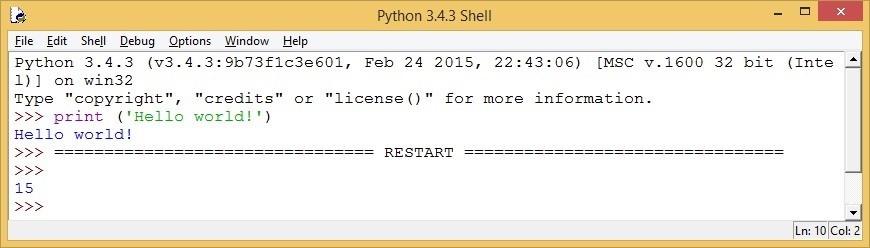
The result will be printed in the IDLE shell window:
Notice how the result of our program was displayed after the RESTART line.
Python course
- Introduction
- Python overview
- Install Python on Windows
- Install Python on Linux
- Add Python to the Windows Path
- Run Python code
- Interactive prompt
- IDLE editor
- Command line
- Help mode
- Basic programs
- Write your first program
- Use comments
- What are variables?
- Variable data types
- Variable names
- Numeric variables
- Strings
- Get the current date and time
- Operators overview
- Arithmetic operators
- Comparison operators
- Logical operators
- Assignment operators
- Membership operators
- Identity operators
- Conditional statements
- The if statement
- Get user input
- The if...else statement
- The if...elif statement
- Nested if statements
- Use logical operators
- Loops
- The for loop
- Use for loop with the range() function
- The break statement
- The continue statement
- The pass statement
- Use else statement in loops
- The while loop
- Nested loop statements
- Errors
- Types of errors
- Syntax and logical errors
- The try...except statements
- The try...except...else statements
- The try...except...finally statements
- Catch specific exceptions
- Raise exception
- Nest exception handling statements
- Modules
- What are modules?
- Import modules
- Find files on disk
- Display module content
- Strings
- What are strings?
- Escape characters
- Access individual characters
- String functions
- Search strings
- Concatenating strings
- Lists, sets, tuples, dictionaries
- What are lists?
- Modify lists
- Loop through a list
- Check whether a value is in a list
- Sorting lists temporarily
- Sorting lists permanently
- Obtaining the list length
- What are sets?
- What are dictionaries?
- Add new key-value pair to a dictionary
- Modify a value in a dictionary
- Delete a key-value pair in a dictionary
- Loop through a dictionary
- What are tuples?
- Looping over a tuple
- Working with files
- How to read and write files
- Read a file
- Read and write – with statement
- Make a list of lines from a file
- Functions
- What are functions?
- Return statement
- Positional arguments
- Keyword arguments
- Default values for parameters
- Flexible number of arguments
- Variable scopes